Master IoT: Top Remote Device Management Software & Examples
Is the Internet of Things (IoT) truly the future, or is it a present reality demanding immediate attention? The surge in interconnected devices across industries necessitates a robust, intelligent approach to management or risk losing the potential benefits of this technological revolution.
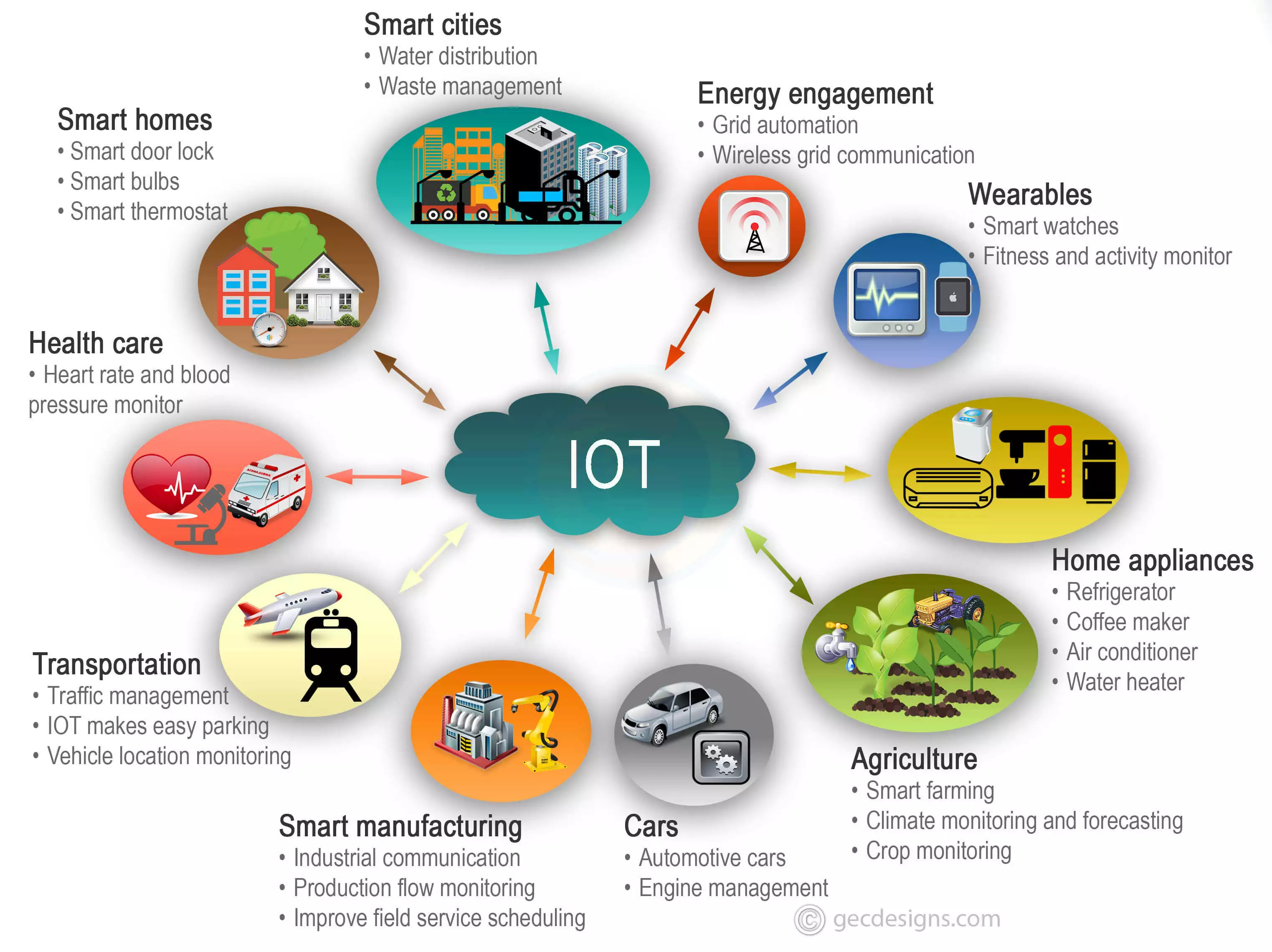
The proliferation of IoT devices has been nothing short of exponential. From smart home appliances to sophisticated industrial sensors, these devices generate vast amounts of data and offer unprecedented opportunities for automation, efficiency, and innovation. However, this rapid growth presents significant challenges. Without effective management strategies, these devices become vulnerable to security breaches, performance degradation, and operational inefficiencies. This article delves into the core of remote IoT device management, exploring its essential components, practical applications, and the advantages it provides.
At its core, IoT device management is a multifaceted process. It encompasses the equipping, validation, configuration, monitoring, and analysis of connected devices within an IoT ecosystem. The ultimate goal is to provide and sustain their functional capabilities, ensuring they operate at peak performance and contribute to the overall objectives of the organization. This comprehensive approach is crucial for maintaining the security, scalability, and overall performance of IoT deployments.
Consider the following scenarios:
- A fleet of delivery trucks equipped with IoT sensors to monitor engine performance, fuel efficiency, and driver behavior.
- A smart factory with hundreds of sensors tracking production processes, machinery health, and environmental conditions.
- A healthcare facility utilizing remote patient monitoring devices to track vital signs and deliver continuous patient care.
In each of these examples, the ability to remotely manage, monitor, and control the devices is paramount to success. Without it, the deployment becomes unmanageable, costly, and prone to failure.
Let's examine some of the key elements that define effective remote IoT device management. This includes:
- Remote Monitoring: The ability to observe the status and performance of devices in real-time, identifying potential issues before they escalate.
- Configuration Management: The ability to remotely configure device settings, ensuring optimal performance and compatibility across the network.
- Security Management: Implementing and enforcing security policies, including access control, encryption, and regular security updates.
- Firmware and Software Updates: Remotely updating firmware and software to patch vulnerabilities, improve functionality, and optimize performance.
- Troubleshooting and Diagnostics: The ability to remotely diagnose and resolve device issues, minimizing downtime and disruption.
To visualize the benefits of Remote IoT Device Management (RIoTDM) here is a table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Remote Monitoring | Real-time observation of device status, performance metrics (CPU usage, memory, etc.) | Proactive issue identification, preventative maintenance, reduced downtime |
| Configuration Management | Remote adjustment of device settings, network configurations, and device-specific parameters. | Consistent device behavior, simplified deployment, efficient scaling |
| Security Management | Implementation and enforcement of security policies, access control, encryption, and remote security updates. | Protection against cyber threats, data integrity, compliance with regulations |
| Firmware/Software Updates | Remote deployment of firmware and software updates to patch vulnerabilities, improve functionality, and optimize performance. | Improved security, enhanced performance, extended device lifespan |
| Troubleshooting/Diagnostics | Remote diagnosis and resolution of device issues, including log analysis and remote control functionalities. | Reduced downtime, faster issue resolution, cost savings on on-site support |
The advantages of adopting remote IoT device management are substantial and span a wide range of industries and applications. Consider the following examples:
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring devices (e.g., wearable ECG monitors, blood pressure cuffs) and smart medical equipment (e.g., smart infusion pumps, connected diagnostic tools) enable continuous patient care, improving health outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- Manufacturing: In smart factories, remote access to industrial equipment allows for predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and optimizing production efficiency. Sensors can be remotely monitored and calibrated, minimizing disruptions and improving product quality.
- Transportation: Fleet management systems rely on remote monitoring and control to track vehicle performance, optimize fuel efficiency, and ensure driver safety.
- Retail: Remote management of point-of-sale (POS) terminals, digital signage, and inventory management systems streamlines operations and enhances the customer experience.
These examples illustrate the versatility of IoT technology and the pivotal role that remote device management plays in unlocking its full potential. As IoT continues to evolve, the ability to securely and efficiently manage devices from a central location will become even more critical.
The following table gives insight of key elements:
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Key Functions | Registration, organization, monitoring, and remote management of IoT devices at scale. |
| Core Capabilities |
|
| Underlying Principles |
|
Remote IoT device platforms are the software solutions that empower the management, monitoring, and control of IoT devices. These platforms serve as the central hub for managing a wide range of devices, from simple sensors to complex industrial equipment.
The following are some of the minimum requirements for any such platform:
- Security: Secure access control, data encryption, and regular security updates are essential.
- Scalability: The platform must be able to handle a growing number of devices and the increasing volume of data they generate.
- Interoperability: Support for various device types, network protocols, and communication standards is crucial.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Real-time monitoring of device health, performance metrics, and the ability to analyze data for insights.
- Remote Management Capabilities: Functionality to configure, update, and troubleshoot devices remotely.
Several remote IoT management software solutions have gained prominence in recent years due to their robust features and ease of use. Each platform offers a slightly different approach, catering to various industry-specific needs and technical requirements. The most popular examples include:
- Microsoft Azure IoT Central: A fully managed SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) solution designed for IoT device management. It provides an intuitive interface for connecting, monitoring, and managing IoT devices. Azure IoT Central supports a wide range of devices and offers advanced analytics and visualization tools.
- AWS IoT Device Management: Part of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) IoT suite, this platform provides a comprehensive set of tools for managing and securing IoT devices. It includes features like device provisioning, over-the-air (OTA) updates, and device monitoring.
- ThingWorx: A comprehensive IoT platform that enables users to build, deploy, and manage IoT applications. It offers robust device management capabilities, including device onboarding, remote monitoring, and secure device connectivity.
Mobile Device Management (MDM) platforms play a significant role in the realm of remote device management, particularly for mobile devices and tablets. MDM solutions are especially valuable for managing corporate-owned or personally-owned devices used for work (BYOD - Bring Your Own Device). The key functions of MDM include:
- Policy Management: Controlling app downloads, data usage limits, and other device settings to ensure compliance and security.
- Software Updates: Deploying software updates and patches to keep devices secure and up-to-date.
- Remote Lock/Wipe: Remotely locking or wiping devices in case of theft or loss, protecting sensitive data.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Monitoring device health, performance, and compliance with corporate policies.
The benefits of MDM are clear:
- Enhanced Security: Protecting corporate data and ensuring compliance with security policies.
- Improved Efficiency: Streamlining device deployment and management, saving time and resources.
- Increased Productivity: Ensuring that remote workers and end-users remain productive by providing seamless access to their enrolled devices.
To properly manage the remote environment it is necessary to ensure some factors, such as the following:
- Network Performance: Ensure reliable and efficient network connectivity for data transmission and instruction reception.
- Interoperability: Address the heterogeneity of IoT devices and their compatibility with various network protocols.
- Data Security: Devices connected to the network become an attractive target for hackers. Therefore, ensuring IoT device protection is one of the most important tasks.
Contextual IoT device management is about addressing the specific needs and variables of a particular application. This approach is made possible by utilizing specialized IoT device management platforms that are tailored for the unique requirements of each application.
Let us explore some specific use cases:
- Smart Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring devices (e.g., wearable ECG monitors, blood pressure cuffs), enable remote health monitoring for continuous patient care. This increases patient satisfaction.
- Smart Industries: Implementing remote access to POS terminals, digital signage, machinery, and sensors. This impacts how you interact with and manage your environment on a daily basis, whether youre at home or at work.
To further illustrate the concepts, consider the following example:
Scenario: A retail company with multiple stores wants to remotely manage its POS terminals. They need to monitor the health of the terminals, deploy software updates, and troubleshoot issues without physically visiting each store.
Solution: The company implements a remote IoT device management platform that allows them to:
- Monitor the performance of each POS terminal, including CPU usage, memory, and storage.
- Remotely install software updates to fix bugs and improve functionality.
- Troubleshoot issues, such as network connectivity problems, without needing to send a technician on-site.
Result: The company saves time and money by reducing on-site visits, improves the security of its POS terminals, and ensures that its systems are always up-to-date and functioning properly.
Remote IoT device management is an essential component of any successful IoT strategy. By providing a centralized platform for managing devices, organizations can improve security, efficiency, and operational performance. The adoption of centralized management platforms is no longer a luxury; it is a necessity for anyone serious about leveraging the power of the Internet of Things.
Here are the key aspects:
- Centralized Management: Manage devices from a single interface, simplifying operations.
- Remote Control: Restart devices over a network.
- Security Focus: Secure access to your devices is a priority, along with device health monitoring.
- Scalability: Enables management of IoT devices at scale.
- Efficiency: Enables stable equipment performance, predictive maintenance, and damage or danger prevention.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces on-site visits and optimizes resource utilization.
- Proactive Maintenance: Allows for predictive maintenance, preventing unexpected outages and optimizing device lifecycles.